P L A N K
The plank is an isometric core stability and foundational movement that when performed correctly, should engage all muscles in the body. Practicing the plank can improve posture and help a person to maintain good balance/stability while doing everyday activities.
Even though athletes from all sports will see an improvement in their athletic performance by practicing planks, here is a small list of sports that require great amounts of core stability & strength:
- Water/snow skiing
- Hockey
- Figure skating
- Gymnastics
- Rowing
- Surfing

C O M M O N F A U L T S
- Elbows placed too far back behind shoulders (should be at 90 degrees)
- Upward curve of body on vertical axis instead of holding body flat
- Inward curve of lower back (lordosis)
- Placing/gripping hands together instead of strait in front with palms flat on ground
- Assumption that placing weight on hands is more challenging than placing weight on forearms (with palms facing down)
E X E R C I S E E X A M P L E S
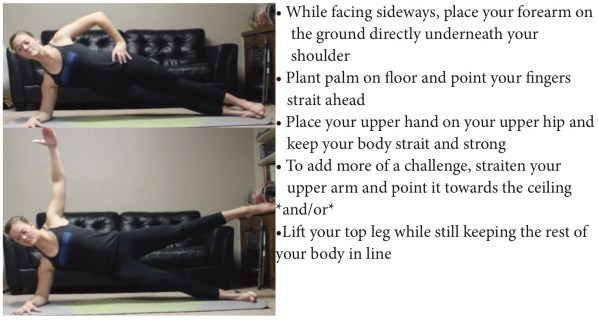
- Side plank: Lift the upper leg if you need more of a challenge
- Supine-facing plank
- Front-facing forearm plank
- Regression: Rest weight on hands with arms strait instead of forearms
Exercise Example: Forearm Plank

- Weight should be placed on forearms with elbows planted directly below shoulders (90 degrees)
- Hands facing flat down & strait out in front of eblows
- Feet placed hip-distance apart
- Flex abdomen (imagine belly button touching the spine)
- Glutes engaged
Exercise Example: Side Plank